Research Lines
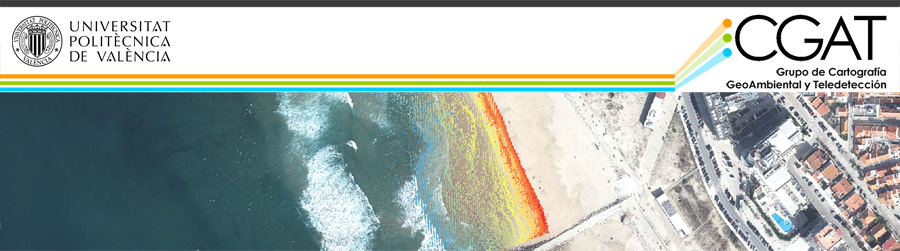
- Beach morphological characterisation from remote sensing
- Shoreline extraction from optical satellite imagery. 3D beach and dune characterisation from LiDAR, UAV and aerial photography. Nearshore bathymetry
- Short and mid-term coastal changes and beach responses to natural events and human impacts
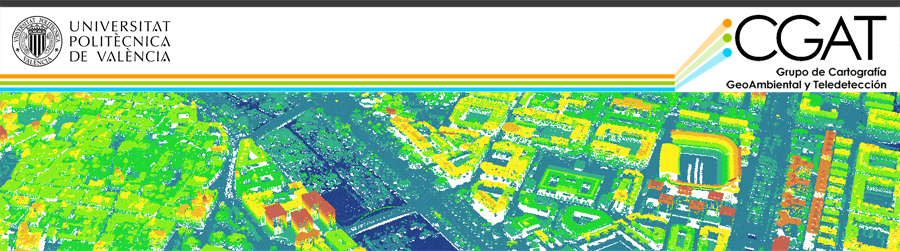
- Land use/Land cover geodatabase updating from high-resolution remote sensing images and LiDAR data using object-based classification techniques
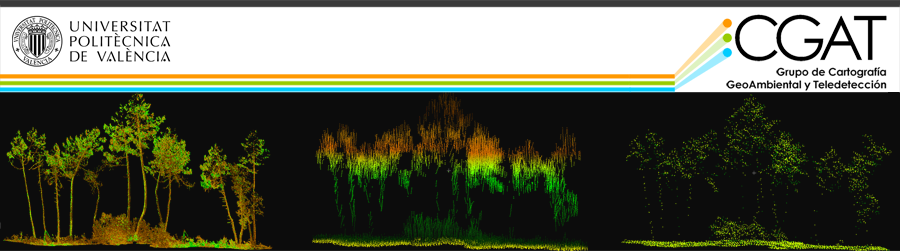
- Analysis of forest structure and fuel mapping from point-clouds (LiDAR, TLS, UAV,…)
- Life Fuel Moisture content estimation and mapping from remote sensing and meteorological data
- Multitemporal urban fragmentation analysis and relations with socio-economic variables
Projects
Current projects

Enhancing higher education e-learning structures and modules in conflict regions of East Africa (101179512)
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 7 others
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2025-2027

Clasificación de nubes de puntos mediante técnicas de Deep Learning (PAID-06-23)
- Financed by: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT)
- Principal Investigator: Pablo Crespo Peremarch
- Duration: 2024-2025
Results:
Peer-Review Journals
Jacon, A.D., Galvão, L.S., Martins-Neto, R.P., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Aragão, L.E., Ometto, J.P., Anderson, L.O., Vedovato, L.B., Silva-Junior, C.H.L., Lopes, A.P., Peripato, V., Assis, M., Pereira, F.R.S., Haddad, I., de Almeida, C.T., Cassol, H.L.G., Dalagnol, R., 2024. Characterizing canopy structure variability in Amazonian Secondary Successions with full-waveform LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2085. DOI: 10.3390/rs16122085

Caracterización de la variabilidad espacio-temporal de los sistemas playa-duna mediante técnicas geomáticas para la adaptación de las costas españolas al cambio climático (PID2023-151587OB-I00)
- Financed by: Spanish State Research Agency
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València, Instituto Geográfico Nacional, Instituto de Hidráulica Ambiental IH Cantabria and Université de Bordeaux
- Principal Investigator: Jesús Palomar Vázquez, Josep E. Pardo Pascual
- Duration: 2024-2026

Sistema de Monitorización Morfosedimentaria de las Playas Valencianas (THINKINAZUL/2021/003)
- Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e innovación with European Union NextGenerationEU (PRTR-C17.I1) and Generalitat Valenciana funds
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València, Universitat de València, Institut Cartogràfic Valencià and Universitat Catòlica de València
- Principal Investigator: Josep E. Pardo Pascual, Jesús Palomar Vázquez
- Duration: 2022-2025

Spectral and Structural 3D Mapping of Mediterranean Fuels for Forest Fire Behavior Modelling [PID2020-117808RB-C21]
- Financed by: Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2021-2025
The main goal of the project is to explore and evaluate the incorporation of 3D structure and field variables derived from LiDAR point clouds, as well as fuel moisture content values from multispectral remote sensing devices into the new physics-based fire behavior models, and the simulation of different scenarios of propagation of wildfires in Mediterranean areas.
Specific objectives:
- Compilation, acquisition and processing of remote sensing data.
- Integration of data in 3D fire behavior models (WFDS).
- Mapping patches and species from different scales and sensors.
- Modelling fuel moisture content.
Results:
Peer-Review Journals
Arcos, M. A., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á., 2024. Evaluating the performance of spectral indices and meteorological variables as indicators of live fuel moisture content in Mediterranean shrublands. Ecological Indicators, 169, 112894. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112894
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Moran, C. J., Seielstad, C. A., Parsons, R. A., Hoff, V., Ruiz, L. Á., Torralba, J., Estornell, J., 2024. Relationships of Fire Rate of Spread with Spectral and Geometric Features Derived from UAV-Based Photogrammetric Point Clouds Fire 7, 132. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7040132
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Almonacid-Caballer, J., Torralba, J., 2024. Class3Dp: A supervised classifier of vegetation species from point clouds. Environmental Modelling & Software, 171, 105859. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105859
Arcos, M., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á., 2023. Analyzing Independent LFMC Empirical Models in the Mid-Mediterranean Region of Spain Attending to Vegetation Types and Bioclimatic Zones. Forests, 14 (7), 1299. Doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071299
Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2022. Analyzing TLS Scan Distribution and Point Density for the Estimation of Forest Stand Structural Parameters. Forests, 13(12), 2115. Doi: 10.3390/f13122115
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Torralba, J., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2022. Classification of Mediterranean Shrub Species from UAV Point Clouds. Remote Sensing, 14 (1), 199. Doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010199
Conference Papers
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz, L. Á., Estornell, J., Simó-Martí, M., Quille-Mamani, J. A., Torralba, J. 2024. Comparación de biomasa estimada a partir de mediciones clásicas y nubes de puntos UAV clasificadas mediante Class3Dp. XX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección y Cambio Global: Retos y Oportunidades para un Crecimiento Azul, pp. 219-222, 4-7 Jun., Cádiz.
Simó-Martí, M., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz, L. Á. 2024. Integración de datos LiDAR en modelos físicos de comportamiento del fuego para la simulación y el estudio de incendios forestales en el bosque mediterráneo. XX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección y Cambio Global: Retos y Oportunidades para un Crecimiento Azul, pp. 269-272, 4-7 Jun., Cádiz.
Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P. 2024. Análisis multitemporal de la estructura vertical de ecosistemas forestales mediterráneos mediante datos TLS. XX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección y Cambio Global: Retos y Oportunidades para un Crecimiento Azul, pp. 291-294, 4-7 Jun., Cádiz.
Ruiz, L.Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Arcos-Villacís, M. A., Torralba-Pérez, J., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Recio, J.A., 2023. The role of Remote Sensing in Fuel Characterization for Wildfire Prevention. International Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change (DRRCC-2023), pp. 166-174, 7 Oct., Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
Torralba, J., Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., 2023. Laser scanner and UAV high-density point clouds for forest inventory and management. XVII GIS in Central Asia Conference (GISCA 2023), 30-31 May, Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan.
Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2022. Modelling and mapping forest structure from aerial LiDAR data. International Symposium on Disaster Risk Reduction, Mitigation and Environmental Sciences (UN4DRR 2022), 21 Jul., Bogor (Indonesia).
Arcos, M. A., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á. 2022. Modelos de regresión para la estimación de la humedad de combustible vivo en la Comunitat Valenciana empleando información satelital. IX Congreso I+D+i Campus d’Alcoi – Creando Sinergias, pp. 97-100, 13-14 Jul. 2022, Alcoi, Spain.
Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Almonacid-Caballer, J. 2022. Estimación de parámetros forestales en Pinus halepensis Mill. a partir de nubes de puntos TLS, UAV y fusión TLS-UAV. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Arcos, M. A., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á. 2023. Live fuel moisture content modeling and mapping using spectral, meteorological and topographic data. Ninth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2023), 3-5 Apr., Larnaca, Cyprus.
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Torralba, J., Estornell, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2022. Análisis de variables extraídas de nubes de puntos fotogramétricas derivadas de imágenes UAV para la clasificación de especies arbustivas. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Arcos, M. A., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á., 2022. Análisis de la influencia de la especie en la estimación de la humedad de combustible vivo mediante índices espectrales derivados de imágenes Sentinel-2. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Arcos, M. A., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á., 2022. Influencia de la fracción de cabida cubierta de las especies forestales en la estimación del contenido de humedad de combustible vivo usando técnicas de teledetección. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Costa-Saura, J. M., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L. Á., Pardo-Pascual, J. E., Soriano-Sancho, J.L., 2022. Live Fuel Moisture Estimation Using Sentinel 2 Data in Non-Monospecific Mediterranean Shrublands. The Third International Conference on Fire Behavior and Risk, 3-6 May, Sardinia(Italy).
Software
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz , L. Á., Estornell Cremades, J., 2023. Class3Dp.
Datasets
Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2025. Field data from forest inventory plots in the Sierra de Espadán Natural Park.
Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2025. Field data from forest inventory plots in the Sierra Calderona Natural Park.
Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2025. Terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) data from forest inventory plots in the Sierra Calderona Natural Park .
Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2025. Terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) data from forest inventory plots in the Sierra de Espadán Natural Park.
Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2025. UAV-based digital aerial photogrammetry (UAV-DAP) of the Sierra Calderona Natural Park.
Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., 2024. Full-waveform ALS dataset of Sierra Espadán Natural Park (Valencia, Spain) (2/2).
Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., 2024. Full-waveform ALS dataset of Sierra Espadán Natural Park (Valencia, Spain) (1/2).
Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., 2024. Discrete ALS dataset of Sierra Espadán Natural Park (Valencia, Spain).
Ruiz, L. Á., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., 2024. Full-waveform and discrete ALS dataset of Sierra Calderona Natural Park (Valencia, Spain).
Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. Á., 2023. RGB and multispectral point clouds of the Sierra Calderona Natural Park.
Workshops

GEOinformation educational resources for CLImate Change Management
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 5 others
- Principal Investigator at UPV: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2022 – 2025
GeoCLIC overall aim is to increase analytic and professional skills among students and Lifelong learners to improve their competencies in CCM through use of GIS and RS tools online. Herein, GeoCLIC introduces the Work-based learning approach to develop training projects and internships in areas impacted by Climate Change. A particular priority is to motivate participation of female learners. 5 modules and OERs (Open Educational Resources) related to CCM will be developed and further enhanced by the use of innovative online learning tools and international collaboration. Employability skills will be boosted by hands-on practices and direct contact with employers. To transfer the project benefits to society, multiple interactions between educators, researchers, environment companies/NGOs and decisionmakers are planned.
Objectives:
- Fostering employability among enrolled and unemployed graduates as CC analyst in earth observation, GIS/RS sector. The project will promote employment in CCM through GIS/RS among recent graduates emphasizing female participation.
- Strengthening cooperation GIS/RS enterprise and universities – Enhancing digital readiness and digital skills across institutions -Supporting a community of practice on CCM through a platform.
- Ensure adequate quality to the OERs developed (R3) through valid certifications (R5) and proper quality assurance methods.
Links:
Recent past projects

Developing Interdisciplinary Postgraduate Programmes and Strengthening Research Networks in Geoinformation Technologies in Armenia and Kyrgyzstan [617695-EPP-1-2020-1-ES-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP]
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (coordinator) and 13 others
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2021-2024
The main goals of the project are to develop postgraduate Higher Education programmes in Geoinformation Technologies (GIT) and strengthening the links in research and innovation between Higher Education Institutions (HEI), industry and administration in Armenia and Kyrgyzstan.
Specific objectives:
- To identify research and development needs of Kyrgyzstan and Armenia in the field of Geoinformation Technologies (GIT).
- To create a Research Node in GIT per partner country to promote and harmonise collaborative innovation projects and joint research lines
- To improve and/or update research laboratories of GIT.
- To train trainers from partner countries in relevant topics of GIT that have special interest for regional development of innovation and environmental protection.
- To provide teachers and managers from HEI’s in partner countries knowledge and skills in transversal topics of higher education following Bologna process standards.
- To create interdisciplinary postgraduate programmes (courses and joint PhD programmes) that enhance the potential of GIT in different areas and degrees and focus research outputs on contemporary problems at regional and global scales.
- To foster and strength the cooperation between university and industry in those topics identified as critical for the sustainable development of the partner countries.
- To exchange and share experiences and perspectives between two partner countries with similar recent historical background, that are facing some common socio-economic challenges and need to stimulate new strategies in research and development.
Links:

Modeling and Mapping Live Fuel Moisture Content in the Comunitat Valenciana
- Financed by: Red Eléctrica de España S.A.U.
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV-CGAT) and Red Eléctrica de España S.A.U.
- Principal Investigator: Angel Balaguer-Beser
- Duration: 16/12/2020 – 15/12/2023
The aim of this project is to is to develop a precise and robust model for estimating the Live Fuel Moisture Content (LFMC) in the Valencian region of Spain that can be updated almost continuously, based on the records provided by successive medium-resolution satellite images (Sentinel 2, supported by Landsat 8) and the climatic data taken over the territory. This model will produce a series of maps with high spatial resolution to be integrated into a web browser, which could be used by an integrated forest fire management system.
Results:
Peer-Review Journals
Arcos, M., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L.A., 2023. Analyzing Independent LFMC Empirical Models in the Mid-Mediterranean Region of Spain Attending to Vegetation Types and Bioclimatic Zones. Forests, 14 (7), 1299. Doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071299
Conference Papers
Arcos, M., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L.A., 2022. Influencia de la fracción de cabida cubierta de las especies forestales en la estimación del contenido de humedad de combustible vivo usando técnicas de teledetección. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Arcos, M., Edo-Botella, R., Balaguer-Beser, Á., Ruiz, L.A., 2022. Análisis de la influencia de la especie en la estimación de la humedad de combustible vivo mediante índices espectrales derivados de imágenes Sentinel-2. XIX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. Teledetección para una Agricultura Sostenible en la era del Big Data, pp. 189-192, 29 Jun. – 1 Jul., Pamplona.
Arcos, M.; Balaguer-Beser, Á.; Ruiz, L.A., 2021. Modelos empíricos de predicción del contenido de humedad del combustible vivo mediante índices espectrales de Sentinel-2 y datos meteorológicos. III Congreso en Ingeniería Geomática (CIGeo), pp. 239-247, 07-08 Jul., online.

Monitorización de la respuesta de la línea de costa a eventos erosivos y a patrones rítmicos mediante imágenes de satélite (PAID-06-22)
- Financed by: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Principal Investigator: Carlos Cabezas Rabadán
- Duration: 2022-2023

University Network for Disaster Risk Reduction [609592-EPP-1-2019-1-BE-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP]
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 7 others
- Principal Investigator at UPV: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2020-2023
The overall aim of the UN4DRR project is to modernize the courses related to Disaster Risk Reduction and Management integrating GIS/RS applications as the significant part of the course content. The long-term effect will be to educate future experts for prevention and management of natural and human-induced disasters (e.g. fires) in the Indian Ocean Rim supporting national and EU policies. The project encourages the cooperation with national authorities, public and private sector offering joint DRRM initiatives and access to short courses for use of GIS/RS via online/offline mode. The project also motivates a more proactive cross-region dialogue in DRRM related educational program in the realization of capacity building and internationalization.
Specific objectives:
- Establish appropriate train-the-trainer program for curriculum development following Bologna standards and ECTS comparability in DRRM.
- Purchase and installation of GIS/RS equipment at each IOR (Indian Ocean Rim) partner HEI.
- Improve the research and practical skills of graduate/postgraduate students making use of state-of-the-art GIS/RS methods for DRRM.
- Deliver short modules online/offline on GIS/RS for DRRM for public and private sector.
- Embed a culture of quality to the project, its outputs and outcomes.
- Facilitate adequate management tools for the correct implementation of the project.
Links:

Monitorización morfológica de las playas utilizando imágenes de satélite de libre acceso y cobertura global (PID2019-111435RB-I00)
- Financed by: Spanish State Research Agency
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Principal Investigator: Josep E. Pardo Pascual
- Duration: 2020-2024

A proof-of-concept for the implementation of a European Copernicus coastal flood awareness system (101004211)
- Financed by: EU
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (coordinator) and 7 others
- Principal Investigator: Josep E. Pardo Pascual
- Duration: 2021-2022

Monitorización de precisión de las fluctuaciones de agua de humedales salinos intermitentes Ramsar en la cuenca media del Ebro mediante teledetección espacial
- Financed by: Fundación Biodiversidad
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València
- Principal Investigator: Josep E. Pardo Pascual
- Duration: 2020-2022

Mejora de la gestión del agua en arrozales de productores rurales peruanos empleando drones y satélites en el marco del cambio climático [2020/ACDE/000307]
- Financed by: Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional para el Desarrollo (AECID)
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (coordinator) and 3 others
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2021-2023
Water is a limiting resource for agricultural production, not only in areas where water availability is scarce, but also in those areas more susceptible to the effects of climate change in the short term, where certain crops may no longer be sustainable. This project aims to develop improvements in the irrigation techniques used in rice cultivation in the Chancay-Lambayeque valley (Peru), with the analysis at local level of images acquired with drones, and at regional level using Sentinel images. This proposal aims to detect anomalies in the crop, identify the presence of pests/diseases and make early estimates of crop production, thus identifying possible deficits affecting food in the region. This project integrates a strong social component, supporting rural producers to sustainably increase production and productivity, introducing gender equality mechanisms to increase the integration of women in agriculture.
Specific objectives:
- Reducing water consumption and bringing the use of technology closer to the target group at local level.
- Training and awareness.
- Rice production estimation and efficient water and phytosanitary management at valley scale.
Links:

Estudio del abandono de tierras utilizando diferentes técnicas de teledetección [AICO-2020-246]
- Financed by: Generalitat Valenciana, through the Conselleria d’Innovació, Universitats, Ciència i Societat Digital (subvenciones para grupos de investigación consolidables)
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT)
- Principal Investigator at UPV: Javier Estornell
- Duration: 01/01/2020 – 31/12/2021
This project aims to detect the abandonment of citrus farmland using different remote observation techniques. Satellite images (Sentinel-2 and WorldView3), three-dimensional data (LiDAR data and 3D point clouds derived from images taken from an unmanned aerial vehicle, UAV) and open access orthophotos were used to identify and to map the abandoned parcels. The estimation of citrus biomass of abandoned trees is analyzed considering dendrometric and remote sensing data.
Results:
Peer-Review Journals
Morell Monzó, S., Sebastiá Frasquet, M.T., Estornell Cremades, J., 2022. Cartography of citrus crops abandonment using altimetric data: LiDAR and SfM photogrammetry. Revista de Teledetección, 59, 47-58. doi: 10.4995/raet.2022.16698
Morell Monzó, S., Sebastiá Frasquet, M.T., Estornell Cremades, J., 2021. Land Use Classification of VHR Images for Mapping Small-Sized Abandoned Citrus Plots by Using Spectral and Textural Information. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 681. doi: 10.3390/rs13040681
Morell Monzó, S., Estornell Cremades, J., Sebastiá Frasquet, M.T., 2020. Comparison of Sentinel-2 and High-Resolution Imagery for Mapping Land Abandonment in Fragmented Areas. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 2062. doi: 10.3390/rs12122062

Identifying Marginal Lands in Europe and strengthening their contribution potentialities in a CO2 sequestration strategy [823805 MAIL-H2020-MSCA-RISE-2018]
- Financed by: EU Research and Innovation programme Horizon 2020. Marie Skłodowska-Curie/RISE action
- Partners: Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUT) (coordinador), Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 4 others
- Principal Investigator at UPV: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 01/01/2019 – 31/12/2021
Marginal Lands (MLs) could offer suitable carbon sinks by afforestation/reforestation projects without being competitive to food production, conforming to EU/Global policies. The main objective of MAIL is to trigger utilization of MLs as Carbon Sinks by activities related to forestry and agriculture. The project aims to detect and classify mountainous and semi-mountainous Marginal Lands (m/sm MLs), in order to deliver a web-based regional platform with data, methodology and applications which will be valuable for policy makers, stakeholders or researchers.
MAIL will assess MLs’ presence, distribution and suitability in smart and efficient way, considering that marginality differs within European bioclimatic zones. It will detect MLs through multiple layer analysis of existing EU/Global scale datasets (land cover, land use, soil or climatic information, etc.) and will further examine, validate and classify MLs, through field stratified sampling, into Carbon sequestration capacity categories.
In pilot areas MAIL will augment the achieved accuracy by using enhanced spatial and radiometric resolution of full free and open access satellite datasets. Furthermore, it will propose actions that have to be taken in order to increase Carbon sequestration capacity and it will evaluate their feasibility by using a set of criteria for accurate cost estimation. Finally, it will deliver developed methodologies, algorithms and techniques on a web-application platform for on-demand production of thematic maps within Europe.
Objectives:
- Definition of parameters describing Marginal Land within the different European climate zones, as MLs are affected by latitude.
- Implementation of certain series of data processing in order to determine the best possible way to map/monitor m/sm MLs based on free available datasets, satellite data or open source applications.
- Quantification of potential CO2 sequestration capacity and sustainable utilization of MLs under the prism of LULUCF.
- Alternative proposals of possible vegetation species that might be used for CO2 storage on MLs considering the limited site conditions. To test the effectiveness of the methodology of the project, the approach will be applied in pilot case studies, representative of Mediterranean and Central/Central-Eastern Europe.
- Creation of a knowledge base and a virtual web classroom for the training of participants in advanced classification remote sensing techniques.
- Creation of a virtual place where partners, stakeholders or research community, could collaborate and find useful information.
- Establishment of a permanent working team consisting of RS and Forestry experts that will focus on the MLs management at EU level.
- General guidelines and manuals will attract and help relevant stakeholders. The pilot work will prove the feasibility of MAIL results. The project will focus on initiating the supply chain, analyzing, describing and implementing possible planting and harvesting methods as well as logistic concepts.
Links:
Results:
Conference Papers
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Torralba, J., Ruiz, L. A., 2022. Generación de un curso en línea masivo y abierto (MOOC) como resultado de una acción Marie Skłodowska-Curie. VIII Congreso de Innovación Educativa y Docencia en Red, pp. 1291-1299, 6 – 8 Jul., Valencia.
Torralba, J., Ruiz, L.A., Georgiadis, C., Patias, P., Gómez-Conejo, R., Verde, N., Tassapoulou, M., Bezares, F., Grommy, E., Aleksandrowicz, S., Krätzschmar, E., Krupiński, M., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., 2021. Methodological proposal for the identification of marginal lands with remote sensing-derived products and ancillary data. III Congreso en Ingeniería Geomática (CIGeo), pp. 239-247, 07-08 Jul., online.
Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L.A., Abad, A., Felten, B., Torralba, J., 2021. A review of the use of remote sensing for monitoring and quantifying carbon sequestration in marginal lands. III Congreso en Ingeniería Geomática (CIGeo), pp. 239-247, 07-08 Jul., online.
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. A., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2021. Machine learning applied to the classification of riverine species using UAV-based photogrammetric point clouds. First International Conference on Smart Geoinformatics Applications (ICSGA), pp. 33-36, 24-25 Feb., online.
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. A., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2020. Classification of UAV-based photogrammetric point clouds of riverine species using machine learning algorithms: a case study in the Palancia river, Spain. ISPRS Archives: XXIV ISPRS Congress (Volume XLIII-B3-2020), pp. 575–582, 31 Aug. – 2 Sep. online, Nice, France.

Desarrollo de técnicas de monitorización de superficies agrarias de la Comunitat Valenciana
- Financed by: Generalitat Valenciana, through the Consellería de Agricultura, Desarrollo Rural, Emergencia Climática y Transición Ecológica (Línea nominativa S847000)
- Partners: Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV-CGAT), Conselleria d’Agricultura, Desenvolupament Rural, Emergència Climàtica i Transició Ecològica de la Generalitat Valenciana, and Institut Cartogràfic Valencià
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 01/01/2018– 31/12/2021
The aim of this project is to develop and evaluate methodologies for monitoring agricultural crops in the Valencian Community using available satellite images from the European Earth Observation Programme Copernicus, and aerial orthoimages provided by the Institut Cartogràfic Valencià. In particular, the crop monitoring mainly consists on the classification of crop types using machine learning techniques, including confidence index, and the identification of abandoned parcels. The results are evaluated using ground truth sampled in the terrain.
Results:
Conference Papers
Ruiz, L. A., Almonacid-Caballer, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Recio, J. A., Pardo-Pascual, J. E., Sánchez-García, E., 2020. Automated classification of crop types and condition in a Mediterranean area using a fine-tuned convolutional neural network. ISPRS Archives: XXIV ISPRS Congress (Volume XLIII-B3-2020), pp. 1061–1068, 31 Aug. – 2 Sep. online, Nice, France.

NEXUS
The Nodes of Excellence in (SEA) Universities through Spatial Data [585604-EPP-1-2017-1- BE-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP]
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) (coordinator),
- Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 9 others
- Principal Investigator at UPV: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 2019-2021
The NEXUS project is an Erasmus + CBHE (Capacity Building in High Education) proposal whose main aim is to enhance the research capacities of HEIs in the southeast Asian region, by strengthening relationships between Education, Research and Innovation in GIS, SID and remote sensing, for applications that are related to environment, agriculture and situations of emergency. The project will develop a common nexus between various actors of research and innovation (HEIs, research centers, spin-off companies) in Thailand, Myanmar and Cambodia where specific methodologies for innovation transfer are convergent with EU developments in accordance with Europe 2020 strategy and Smart specialisation initiatives which is a new engine to boost R&D growth and subsequently job opportunities and business creation. This will improve the transfer of innovation from universities to local and regional enterprises, enhancing their innovation potential for geodata use and generating new applied research.
Overall objective:
- The broad goal of NEXUS is to combine industrial, educational and innovation resources in targeted countries and regions of South East Asia (Thailand, Myanmar and Cambodia) to create opportunities for knowledge-based investments while increasing research capacity of HEIs through GIS and remote sensing technology.
Specific objectives:
- Develop conceptual framework and structure for smart specialisation and innovation in GIS/remote sensing in targeted SEA (SouthEast Asia) countries
- Support the research capacity of partner institutions in emerging topics that contribute to updating university study programmes at Ph.D.and Post Doc levels
- Design a strategy for imparting ‘hands-on’ practical training of delivering applied research outputs and working with identified business companies
- Create an innovation network and hub that enhances the use of GIS/remote sensing for societal uses
Links:

FIRMACARTO
Analysis and assessment of forest structure parameters from LiDAR and other emergent techniques for modeling fuel potencial (FIRe MAnagement CARtographic TOols)) [CGL2016-80705-R]
- Financed by: Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and FEDER
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT)
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 30/12/2016 – 29/12/2019
Wildfire prediction and behaviour models require more precise information concerning forest structure, in particular that concerning understory vegetation. New data acquisition techniques should be adapted to provide the right information at affordable costs, and allowing for the integration of data acquired at different scales. The main goal of this project is to explore methods to acquire and process LiDAR data and other emergent terrestrial and aerial remote sensing techniques to a higher level of detail, to develop methods for the estimation of forest fuel variables required in the new models of fire prediction and behaviour, and to integrate them for the design of efficient protocols, data processing and analysis, and their application to the characterization of fuel potential.
For this purpose, new methods for LiDAR full-waveform processing will be developed, and their potential for understory vegetation characterization in Mediterranean areas evaluated. The potential of terrestrial laser scanner as a reference measure will be analysed, as well as its complementarity with hemispheric photography systems. Cloud points generated by optical cameras and low-cost UAS-LiDAR systems will be analysed and processed for the generation of canopy structural variables. Parameters obtained using different technologies (aerial and UAS-LiDAR, TLS, hemispheric cameras, dense image matching-UAS) will be tested for fuel modelling and wildfire behavior.
Objectives:
- Increase LiDAR full-waveform applicability by exploring its potential to characterize understory vegetation
- Study the potential of TLS as reference and calibration of understory aerial measurements, and complementarity with hemispheric photography
- Acquisition and processing of point clouds from UAV optical cameras (SfM) for using in fuel and fire behavior models
- Analysis of potential of low-cost UAS-LiDAR sensors for high detail (hot spots) forest structure characterization:
- Integration of metrics for using as input in fire behavior models
Results:
Peer-Review Journals
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Fournier, R.A., Van-Tho, Nguyen, van Lier, O.R., Ruiz, L.A., 2020. A comparative assessment of the vertical distribution of forest components using full-waveform airborne, discrete airborne and discrete terrestrial laser scanning data. Forest Ecology and Management, 473, 118268. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118268
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., 2020. A full-waveform airborne laser scanning metric extraction tool for forest structure modelling. Do scan angle and radiometric correction matter? Remote Sensing, 12(2), 292. doi: 10.3390/rs12020292
.Crespo-Peremarch, P., Tompalski, P., Coops, N., Ruiz, L.A., 2018. Characterizing understory vegetation in Mediterranean forests using full-waveform airborne laser scanning data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 217, pp. 400-413. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2018.08.033
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A.,Balaguer-Beser, Á., Estornell, J., 2018. Analyzing the role of pulse density and voxelization parameters on full-waveform LiDAR-derived metrics. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 146, pp. 453-464. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.10.012
Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L. A., 2018. Assessing the use of discrete, full-waveform LiDAR and TLS to classify Mediterranean forest species composition. Revista de Teledetección, 52, 27-40. doi:10.4995/raet.2018
Conference Papers
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. A., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2021. Machine learning applied to the classification of riverine species using UAV-based photogrammetric point clouds. First International Conference on Smart Geoinformatics Applications (ICSGA), pp. 33-36, 24-25 Feb., online.
Ruiz, L. A., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., 2021. Modelling canopy fuel properties and understory vegetation with full-waveform LiDAR. First International Conference on Smart Geoinformatics Applications (ICSGA), pp. 29-32, 24-25 Feb., online.
Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L. A., Torralba, J., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2020. Classification of UAV-based photogrammetric point clouds of riverine species using machine learning algorithms: a case study in the Palancia river, Spain. ISPRS Archives: XXIV ISPRS Congress (Volume XLIII-B2-2020), pp. 659-666, 31 Aug. – 2 Sep. online, Nice, France.
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., Carbonell-Rivera, J. P., Ruiz, L. A., 2020. Comparing the generation of DTM in a forest ecosystem using TLS, ALS and UAV-DAP, and different software tools. ISPRS Archives: XXIV ISPRS Congress (Volume XLIII-B3-2020), pp. 575–582, 31 Aug. – 2 Sep. online, Nice, France.
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., 2019. Analysis of Side-Lap Effect and Characterization of Understory Vegetation Using Full-Waveform ALS. II Congreso en Ingeniería Geomática, 26-27 Jun., Madrid. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019019006
Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Estornell, J., Ruiz, L.A., Torralba, J., López-Cortés, I., Salazar, D., 2019. Comparación de medidas de Nerium oleander L. mediante medición clásica, láser escáner terrestre (TLS) e imágenes derivadas de drones (UAV). Hacia una visión global del cambio climático. XVIII Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección., pp. 81-84, 24-27 Sept., Valladolid.
Torralba, J., Ruiz, L.A., Carbonell-Rivera, J.P., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2019. Análisis de posiciones y densidades TLS (Terrestrial Laser Scanning) para optimizar la estimación de parámetros forestales. Hacia una visión global del cambio climático. XVIII Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección., pp. 443-446, 24-27 Sept., Valladolid.
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., 2018. Influence of LiDAR full-waveform density and voxel size on forest stand estimates. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2018: Observing, Understanding and Forecasting the Dynamics of Our Planet, 23-27 July, Valencia.
Ruiz, L.A., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Torralba, J., 2018. Aplicación del LiDAR full-waveform en la modelización de propiedades de combustibilidad de la cubierta arbórea y el sotobosque. Workshop LiDAR aplicado a los incendios forestales, 19 Oct., Alcalá de Henares.
Torralba, J., Ruiz, L.A., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Fernández-Sarría, A., 2018. Variables de combustibilidad en bosques mediterráneos mediante láser escáner terrestre: estudios preliminares. Workshop LiDAR aplicado a los incendios forestales, 19 Oct., Alcalá de Henares.
Ruiz, L.A., Crespo-Peremarch, P., 2017. Optimizing operational parameters in a full-waveform LiDAR processing tool for forestry. 17th Symposium on Systems Analysis in Forest Resources (SSAFR 2017), 27-30 Aug., Suquamish, WA, USA.
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., 2017. Análisis comparativo del potencial del ALS y TLS en la caracterización estructural de la masa forestal basado en voxelización. Nuevas plataformas y sensores de teledetección, XVII Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección., pp. 131-135, 4-7 Oct., Murcia.

HERITAG
Higher Education interdisciplinary Reform in Tourism management and Applied Geoinformation curricula [561555-EPP-1-2015-1-ES-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP]
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (coordinator) and 15 others
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 15/10/2015 – 14/04/2019
The project HERITAG aims to develop an interdisciplinary reform in higher education programmes at master level and continuing education integrating Geo-information Technologies (GIT) applied to cultural heritage documentation, tourism management and entrepreneurship. The project promotes the synergy of three main groups of stakeholders: Universities, industry and Administration. The curricular reform integrates the development of capacities in 3 main national and regional priorities in Georgia and Armenia: Geo-information technologies, cultural heritage preservation and documentation, and fostering tourism business and entrepreneurship.
Objectives:
- To create interdisciplinary master specialities in GIT for cultural heritage and tourism, integrating marketing and entrepreneurship skills oriented to consolidate local industry
- To establish Geoinformation and Tourism Technology centres (GTTC), new GIS laboratories and update existing equipment in partner country universities
- To foster the continuous education in Higher Education institutions
- To re-train academic staff in GIT, tourism management and entrepreneurship:
- To introduce and improve good practices for quality assurance in partner countries universities
- To establish organized links between universities, administration and society
Outcomes:
- Creation of 2 Geoinformation and Tourism Technology Centres for training, documentation and dissemination
- Creation/improvement of GIS laboratories in 4 HEI’s
- Acquisition of modern equipment for GIT in cultural heritage
- 6 intensive training courses for partner country teachers
- 2 Workshops in quality assurance and new teaching methods
- Creation of new master specialities in cultural heritage and tourism
- Development of new course contents and teaching materials
- Creation of 2 continuing education modules per country devoted to update professionals
- Creation of promotional websites
- Celebration of labour market days at HEI’s
- Celebration of a final dissemination conference in Tbilisi (Georgia)
Links:

RESETOCOAST
Remote sensing to coastal changes in order to mitigate climate change impacts [CGL2015-69906-R]
- Financed by: Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia
- Principal Investigator: Josep E. Pardo-Pascual
- Duration: 01/01/2016 – 30/06/2019
Beaches are an environmental, social and economic resource of high importance that can be threatened by sea level rise caused by climate change. For minimizing the impact of these changes it would be necessary to study the response of the beach to different factors. To obtain response models that consider sea rise level sea and coastal storm situations specific information is required being expensive and complex to get for all the beaches since this information (bathymetry, slope, beach material texture) changes over time and energy conditions to which they are subjected.
This project aims to use the massive data related to the large series of medium-resolution images (such as Landsat and Sentinel-2) to characterize the evolution of the beaches in large areas obtaining key parameters that allow to analyze how climate change affects to the beaches.
In this project we propose to apply an own algorithm -Shoreline Extraction from Landsat Imagery, SELI- already published and used in previous work as basis for deriving new information using multiple archive Landsat images (series 5, 7 and 8) and those that are being registered by active satellites such as Landsat (7 and 8) and the new European satellite Sentinel-2 (in orbit and operating since June 2015). This set of data will allow us to characterize the evolution of the beaches and to obtain relevant information being expensive for large areas such as the slope of the beachfront or beach material texture.
Another objective of this research is to take advantage of some improvements in Landsat 8 satellite (new band 1 for coastal applications) trying to obtain bathymetry of shallow water next to the coast. To do this the classic algorithms will be applied to Landsat 8 images in a more efficient and accurate way according to the already published results. The bathymetric information-and its variation due to the waves- is extremely important to predict the response of the beaches to rough weather or sea level rise. In addition, all this information may be important to understand how populations of some species living in these highly changing environments are evolving.
The results obtained in this project can be of great interest to environmental, social and economic management of Spanish beaches, particularly for the Mediterranean ones. If objectives were reached, key information for beaches will be obtained (evolution and morphosedimentary features) in an quick and global way with lower costs what could face new and more rigorous studies on areas not yet analyzed.

ForeStructure
Characterization of forest structure by integrated analysis of methods based on LiDAR, terrestrial laser scanning and imagery [CGL2013-46387-C2-1-R]
- Financed by: Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and FEDER
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT); Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM-Silvanet)
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 01/01/2014 – 31/12/2016
The analysis of forest structure is crucial for biomass estimates and carbon flux monitoring, for forest inventories, and for forest fuel mapping as input in wildfire risk models. Methods using LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for forest structural and fuel variables estimation have an operational use, however, some aspects must be solved: (i) the development of LiDAR full waveform processing methods, with more potential for structure study; (ii) methods for cartography of forest inventories and management, and stratification of structural types using LiDAR and imagery, (iii) the procedures to improve estimates of diameters at plot level by developing models, (iv) the estimation of fuel attributes using LiDAR full waveform; (v) the estimation od errors in prediction models at small stands levels; (vi) the acquisition configuration and possibilities of TLS; and (vii) the integration of data and models. As a result of these goals and actions, tools useful for forest management at national level are developed, to contribute for the improvement of wildfire prediction and fire behavior.
Objectives:
- Development of specific tools for LiDAR full-waveform processing and analysis
- Development and evaluation of methods for the stratification of structural fuel types from LiDAR, high and medium resolution satellite imagery using object-based analysis
- Study and comparison of structure and fuel variables models from discrete and full-waveform LiDAR data, and analysis of methodological parameters
- Analysis of field data acquisition with terrestrial laser scanner (TLS):
- Analysis of spatial configuration and acquisition parameters
- Study of methods for prediction of structure and fuel variables from TLS
- Integration of data and methods and future research
Results:
Ruiz, L.A., Recio, J.A., Crespo-Peremarch, P., Sapena, M., 2018. An object-based approach for mapping forest structural types based on low density LiDAR and multispectral imagery. Geocarto International, 33(5), pp. 443-457. doi:10.1080/10106049.2016.1265595
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., Balaguer-Beser, A., 2016. A comparative study of regression methods to predict forest structure and canopy fuel variables from LiDAR full-waveform data. Revista de Teledetección, Special issue: Active Remote Sensing in Forest Applications. pp. 27-40. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4995/raet.2016.4066.
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., Balaguer-Beser, A., Estornell, J., 2016. Analysis of the side-lap effect on full-waveform LiDAR data acquisition for the estimation of forest structure variables. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., 12-19 July, Prague, XLI-B8, pp. 603-610. doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLI-B8-603-2016
Crespo-Peremarch, P., Ruiz, L.A., Balaguer, A., Estornell, J., 2015. Análisis temporal de la estructura forestal mediante métricas derivadas de LiDAR full-waveform. Actas del XVI Congreso Nacional de la Asociación Española de Teledetección, 21-23 Oct., 2015, Sevilla.
Final dissemination workshop on LiDAR technologies for forest structure assessment
ACTUALIS
Development and Integration of Methods for Land Use/Land Cover Database Updating [CGL2010-19591/ BTE]
- Financed by: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación and FEDER
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT)
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 01/01/2011 – 31/12/2013
Land use/Land cover (LULC) databases are essential information for applications such as natural resources or territory management and landscaping. Their maintenance is expensive and the updating rate must be dynamic. New LULC database updating procedures based on object-oriented methods for feature extraction, classification and change detection, were developed and evaluated. Image analysis methods were focused on the extraction of information from cartographic objects (parcel, plot) at the spectral, textural, structural, shape, intra-object and inter-object levels. The use and quality requirements of LiDAR data was analysed for extraction of 3D structure of landscape elements. Object-oriented change detection and classification techniques from a multivariate and multiscale perspective were evaluated in three landscape strata: urban, agriculture-forestry, and mixed areas.
Objectives:
The goal of this project was to develop, integrate and evaluate new LULC database updating procedures, based on object-oriented methods for feature extraction, classification and change detection, integrating a wide spectrum of georreferenced data and facilitate the progressive automatization of the spatial database updating tasks. In addition, multiscale thematic generalization methods were studied from a multiscale perspective in order to optimize the use of available data and their mutual relationship.
Results:
Gil-Yepes, J.L., Ruiz, L.A., Recio, J.A., Balaguer-Beser, A., Hermosilla, T., 2016. Description and validation of a new set of object-based temporal geostatistical features for land-use/land-cover change detection. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing , 121, pp. 77-91. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.08.010
Hermosilla, T., Palomar-Vázquez, J., Balaguer-Beser, A., Balsa-Barreiro, J., Ruiz, L.A., 2014. Using street based metrics to characterize urban typologies. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 44, pp. 68-79. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.12.002
Dimov, D., Palomar, J., Ruiz, L.A. Automated generalization of land-use data with GIS-based programming. gis.SCIENCE – Journal for Geoinformatics. Wichmann, 3 (2014), pp. 109-120.
Recio, J.A., Hermosilla, T., Ruiz, L.A., Palomar-Vázquez, J., 2013. Automated extraction of tree and plot-based parameters in citrus orchards from aerial images. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 90, pp. 24-34. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2012.10.005
Balaguer-Beser, A., Ruiz, L.A., Hermosilla, T., Recio, J.A., 2013. Using semivariogram indices to analyse heterogeneity in spatial patterns in remotely sensed images. Computers and Geosciences, 50, pp. 115–127. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.08.001
Hermosilla, T., Ruiz, L.A., Gil-Yepes, J.L., Recio, J.A., Pardo-Pascual, J.E., 2013. Multi-level object-based urban mapping from remote sensing and GIS data. Symposium GIS Ostrava 2013 – Geoinformatics for City Transformation. 21–23 January, 2013, Ostrava, Czech Republic.
Gil-Yepes, J.L., Hermosilla, T., Ruiz, L.A., Recio, J.A., Balaguer-Beser, A., 2013. Estudio de técnicas de detección de cambios basadas en la clasificación directa de objetos para la actualización de bases de datos agrícolas. XV Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección. 22-24 octubre, Madrid, Spain.
Hermosilla, T., Ruiz, L.A., Recio, J.A., Cambra-López, M., 2012. Assessing contextual descriptive features for plot-based classification of urban areas. Landscape and Urban Planning, 106, pp. 124-137. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.02.008
Hermosilla, T., Gil-Yepes, J.L., Recio, J.A., Ruiz, L.A., 2012. Change detection in periurban areas based on contextual classification. Photogrammetrie Fernerkundung Geoinformation, 4, pp. 359-370. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1127/1432-8364/2012/0123

INFOREST (I, II)
Development of techniques and methods for a sustainable forest management from Earth observation data [TSI-020100-2009-815]
- Financed by: Ministerio de Industria, Turismo y Comercio and FEDER
- Partners:
- COTESA (Centro de Observación y Teledetección Espacial S.A.U.) (coordinador)
- Universidad de Castilla La Mancha (UCLM)
- Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM)
- Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT)
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 01/06/2008 – 31/12/2010
Development of key information for forest management using Earth observation data at different scales: satellite images, aerial images and LiDAR data. Development of methods and tools for feature extraction, generation of indicators, visualization and management infrastructures.
Objectives:
Extraction of forest dasometric variables from LiDAR data; design and adaptation of algorithms and parameters to optimize prediction models for biomass, volume, basal area, canopy cover, etc., in the testing area.
Results:
Software: Lidex, Software tool for LiDAR data preprocessing, generation of terrain models, feature extraction, creation and testing of prediction models
Ruiz, L.A., Hermosilla, T., Mauro, F., Godino, M., 2014. Analysis of the influence of plot size and LiDAR density on forest structure attribute estimates. Forests, 5(5), pp. 936-957. doi:10.3390/f5050936
Ruiz, L.A., Hermosilla, T., Godino, M., Almonacid, J., Fernández-Sarría, A., Recio, J.A., Gil-Yepes, J.L., Mauro, F., 2011. Procedimiento para la estimación de variables dasométricas a partir de datos LiDAR. Actas del XIV Congreso Nacional de la Asociación Española de Teledetección, 21-23 September, Mieres (Asturias), pp. 129-132.
Gil-Yepes, J.L., Ruiz, L.A., Fernández-Sarría, A., Hermosilla, T., 2012. Detección y localización de árboles en áreas forestales empleando datos LiDAR y ortofotografías. Mapping, 155, pp. 20-26. I.S.S.N.: 1131-9100
Links:

GIDEC
Geographic Information Technology for sustainable Development in Eastern neighbouring Countries [511322-TEMPUS-1-2010-SE-JPCR]
- Financed by: Education, Audiovisual and Culture Executive Agency – European Union
- Partners: Universidad Politécnica de Valencia (UPV-CGAT) and 10 others
- Principal Investigator: Luis A. Ruiz
- Duration: 15/10/2010 – 14/10/2013